ChartFlow
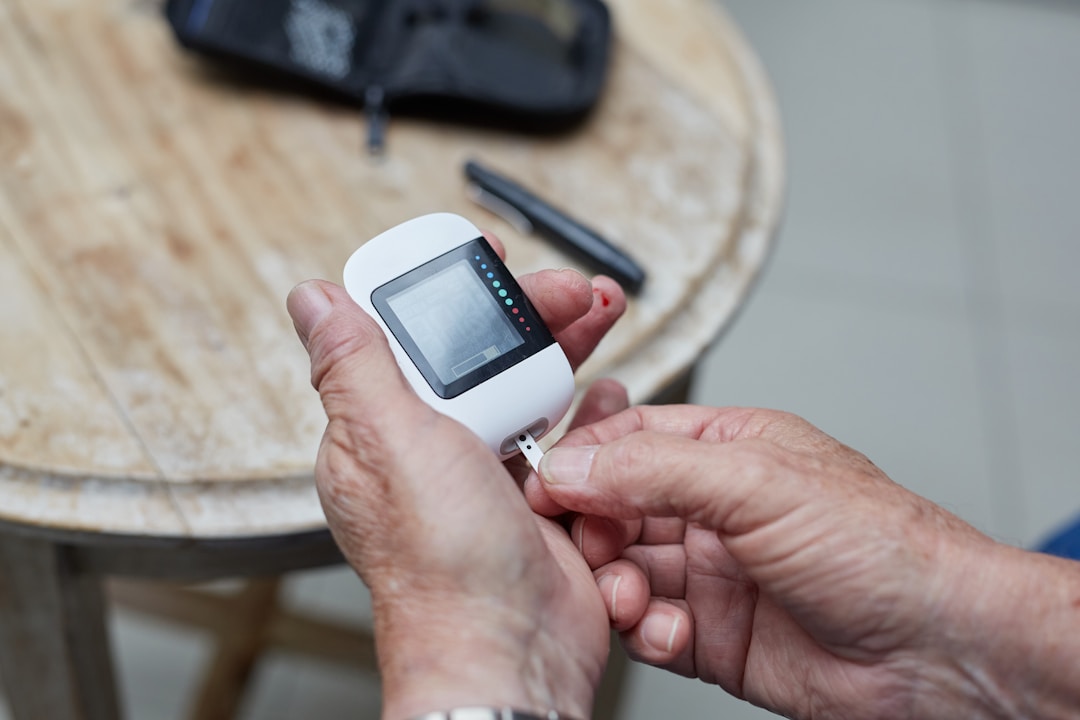
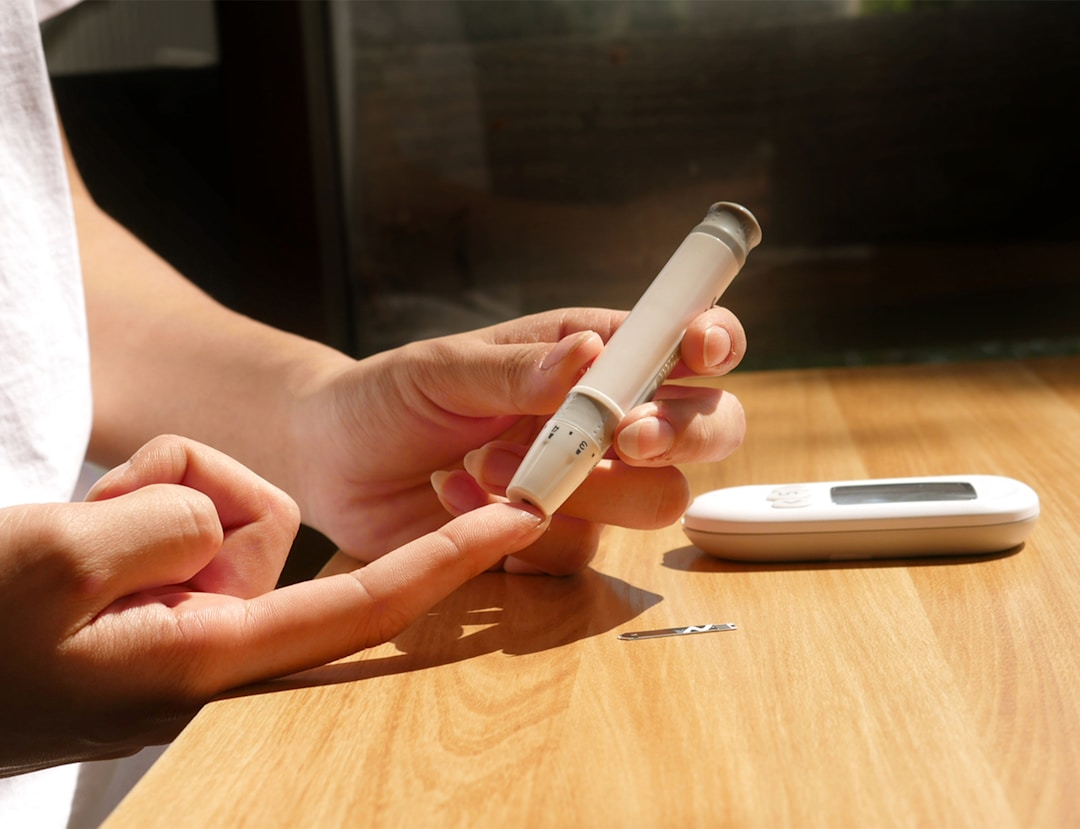
How to use a Glucometer
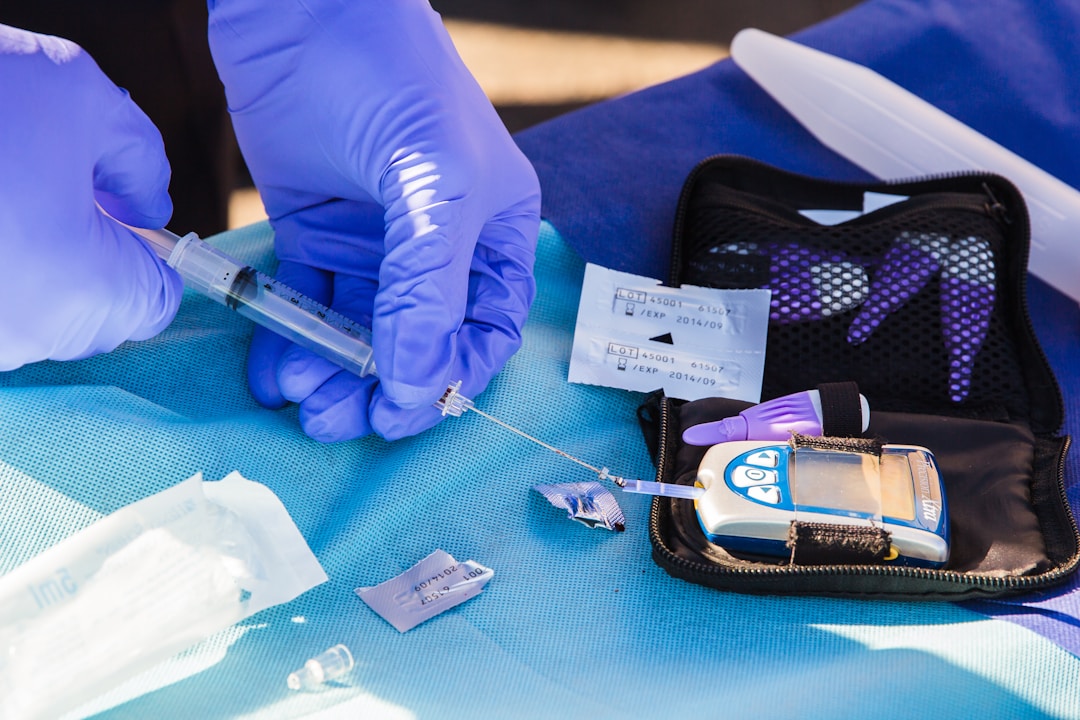
From EMTs all the way to Medical Assistants, RNs, NPs, and Physician Assistants, healthcare workers are often required to check a patient’s glucose. This routine procedure is simple enough that most diabetic patients are comfortable doing regular glucose readings throughout the day without assistance, but you’ll still want to practice handling a glucometer a few times before encountering it in real life.
This diagram (found in our Medication Aide Handbook) should help walk you through the procedure:

The specific cut offs for normal, hyperglycemic, and hypoglycemic ranges may vary by facility but the general guidelines are usually a good rule of thumb:
Normal blood glucose readings:
- Normal adult blood glucose is between 70–110 mg/dL.
- Below 70 is considered hypoglycemic.
- Above 200 is considered hyperglycemic.
Remember, a hypoglycemic patient is experiencing a medical emergency and needs immediate glucose supplementation. If they are conscious and able to swallow, oral glucose solution may be sufficient. If they are unconscious or unable to protect their own airway, IV access should be immediately established.
Note for instructors/schools:
If you’re a Medical Assistant, EMT, or Medication Aide program, we sell simulation packs with pre-built patients and all the supplies needed to complete your labs. These packs can be ordered with, or without, a glucometer for student practice.
More posts like this









_(2)/w=1080,quality=90,fit=scale-down)







/w=1080,quality=90,fit=scale-down)


































/w=1080,quality=90,fit=scale-down)
_(1)/w=1080,quality=90,fit=scale-down)





















/w=1080,quality=90,fit=scale-down)